- DEFINE MEANING OF APERTURE,SHUTTER SPEED,ISO AND DOF
Aperture
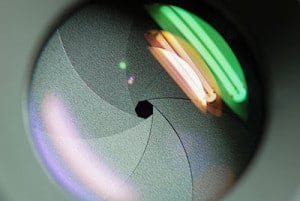
The aperture is a small set of blades in the lens that controls how much light will enter the camera. The blades create a octagonal shape that can be widened (we photogs call it shooting “wide open”), or closed down to a small hole. Obviously, if you shoot with the aperture wide open, then more light is allowed into the camera than if the aperture is closed down to only allow a tiny hole of light to enter the camera.
Shutter Speed
The shutter is a small “curtain” in the camera that quickly rolls over the image sensor (the digital version of film) and allows light to shine onto the imaging sensor for a fraction of a second. The longer the shutter allows light to shine onto the image sensor, the brighter the picture since more light is gathered. A darker picture is produced when the shutter moves very quickly and only allows light to touch the imaging sensor for a tiny fraction of a second. The duration that the shutter allows light onto the image sensor is called the shutter speed, and is measured in fractions of a second. So a shutter speed of 1/2 of a second will allow more light to touch the image sensor and will produce a brighter picture than a shutter speed of 1/200 of a second. So if you’re taking a picture an it is too dark, you could use a slower shutter speed to allow the camera to gather more light.
ISO
The funny thing about ISO is that it is an acronym, but nobody really knows what it stands for. It is always just called ISO even though it really stands for International Organization for Standardization. Every once in a while, you’ll hear an older photographer pronounce it “I-so”, but almost everyone pronounces it “I.S.O.” The ISO controls the exposure by using software in the camera to make it extra sensitive to light.
2. )
Two Shot: This is a shot of two peoples (or other individuals) together.
Cut Away (CA): Cutaways are used in the editing process to fill in footage which is different from the main action. B-roll is often used for cut-aways. An example might be a cut away of a bird singing if the shot is focused on a couple in the woods.
Over the Shoulder Shots (OSS) are shot from behind the person towards their subject. Generally the frame is cut off just behind the ear, although there are several variations. A good technique to use to get this shot is to frame the person facing the subject with about one third of the frame.
Point of View (POV): This is an effective shot that gives the audience the feel that you’re seeing it from the eyes of the performer. It is taken from near the eye-level of the actor and shows what he might see. It could be used to give the perspective of other animals too like a frog, a bird, or a fish.
Selective Focus: By using a large aperture value (f/1.4, f/2.0) you will be able to create a shallow depth of field. This effectively leaves one part of the frame in focus while blurring others, such as the foreground or background. When you change the focus in the shot from the foreground to the background you’re doing another advanced camera shot called a rack focus.




